Description
Carob bean gum (locust bean gum – CBG/LBG) is the ground endosperm of the seeds of the carob tree (Ceratonia siliqua L., see Chapter 2). As a natural hydrocolloid of plant origin it contains no chemical additives or residues. CBG (LBG) has a long history as a safe and versatile food additive. Food grade CBG (LBG) is traded as a white to yellowish white, nearly odourless powder of different particle size distribution.
Chemical Structures/properties
Composition and chemical structure
CBG (LBG) consists of 87-88 % (on dry basis) of a high molecular weight carbohydrate (polysaccharide) which belongs to the group of galactomannans (the same as guar and tara gum). The remaining 12-13 % consists mainly of protein and fibrous matter such as residues from the germ, seed coat and cell wall material. The galactomannan CBG (LBG) is composed of mannose and galactose sugar units (approx. ratio 4:1) which are bound through glycosidic linkages. Single galactose residues are attached to a long linear β-mannan backbone chain. Other commercially available galactomannans with similar basic structure are guar gum and tara gum. The formulae in Figure 3.1 show the structural segment of CBG (LBG) and of the related galactomannans guar gum and tara gum. The distribution of galactose residues along the mannan chain is irregular.
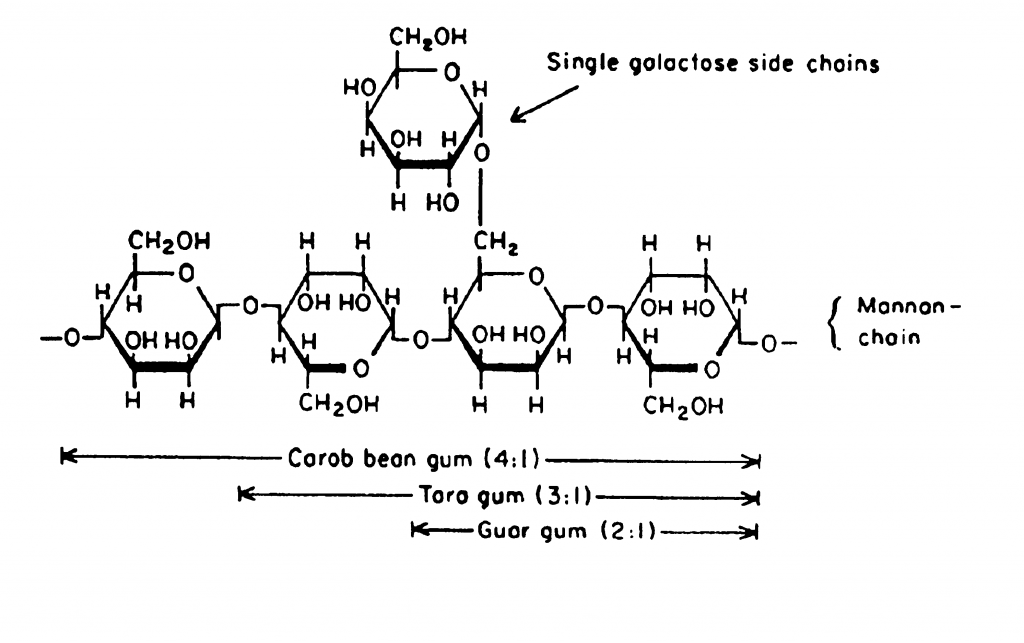
Some of the technologically important properties of galactomannans, e.g. cold water swelling, gelation with other polysaccharides or by self-association, are strongly influenced by the ratio of galactose: mannose as well as by the distribution pattern of the galactose side-chain along the mannan chain.
General properties
Solubility: The most important property of CBG (LBG) is its high water binding capacity as well as the formation of very viscous, stable solutions in high dilution (1% and lower). In contrast to guar gum, which dissolves at room temperature to a very large extent, CBG (LBG) has to be heated to 85-90°C to bring about solution and full viscosity development. The solutions are slightly opaque and remain stable and fluid at room temperature. This is a major advantage over starch solutions and pastes which flocculate or tend to form opaque gels upon standing (retrogradation of starch). Like other hydrocolloids, CBG (LBG) is insoluble in organic solvents. It can be precipitated from aqueous solution by addition of water-miscible solvents like ethanol.
CBG (LBG), like other hydrocolloids, tends to form lumps when added to water or vice versa, and is therefore difficult to dissolve. Lumping is more pronounced with fine powders but if mixed with water soluble solids like sugar or salts, this can be avoided. Wetting with a water soluble organic solvent (e.g. alcohol) can also prevent lumping.
Viscosity of aqueous solutions and the stability in solution: Apart from purity, the viscosity of aqueous solutions of CBG (LBG) is the most important quality criteria. This is usually measured in 1% solutions, (after heating and cooling) with a rotational viscosimeter such as the Brookfield viscosimeter. Galactomannans show non-Newtonian behaviour, e.g., the viscosity decreases with higher shear rates (“shear-thinning”), an effect which also facilitates pumping of the solutions. The viscosity of galactomannan solutions depends on the molecular size and molecular weight distribution, on the manufacturing process and the raw material e.g. kernels, used. The following viscosity ranges are typical for the 1% water solution of the galactomannans (viscosities measured after heating to 85-95°C and cooling to 25°C at 20rpm).
| Carob bean gum | 2500-3500 mPa . s |
| Tara gum | 3800-5200 mPa . s |
| Guar gum | 3500-5500 mPa . s |
Galactomannan solutions are rather stable and show practically no change in viscosity upon standing at room temperature (provided no microbial degradation occurs), slight pH changes or addition of salts. Prolonged heating at high temperature (boiling) reduces the viscosity. Similar to other hydrocolloids, galactomannans can be hydrolysed by microorganisms, consequently solutions should be sterilised or preserved for storage.
Interaction with other polysaccharides: One of the most interesting and useful properties of CBG (LBG) is its interaction with specific hydrocolloids resulting in a substantial viscosity increase or gel formation. The interaction is particularly strong with carrageenan and xanthan gum, producing soft or highly elastic gels, depending on the concentration of the gums. This synergistic effect of CBG (LBG) has found many important applications.
Nutritional information
From a nutritional stand point, CBG (LBG) is regarded as a soluble dietary fibre. As such it is, contrary to starch, not digestible in the digestive tract (small intestine). CBG (LBG) is however partially fermented in the large intestine by microorganisms resulting in gas formation and production of short chain fatty acids (acetate, propionate) and, therefore, providing some energy to the organism. Since the exact digestibility is not yet known, the caloric value of nil is used for CBG (LBG) as well as dietary fibres in general, when calculating the energy value of foods. A discussion of this topic is in progress and a caloric value of 1 or 2 kcal/g can be expected in the future.